Basic System Design Notes
Just like my other notes, the information here can continue to grow.
Introduction
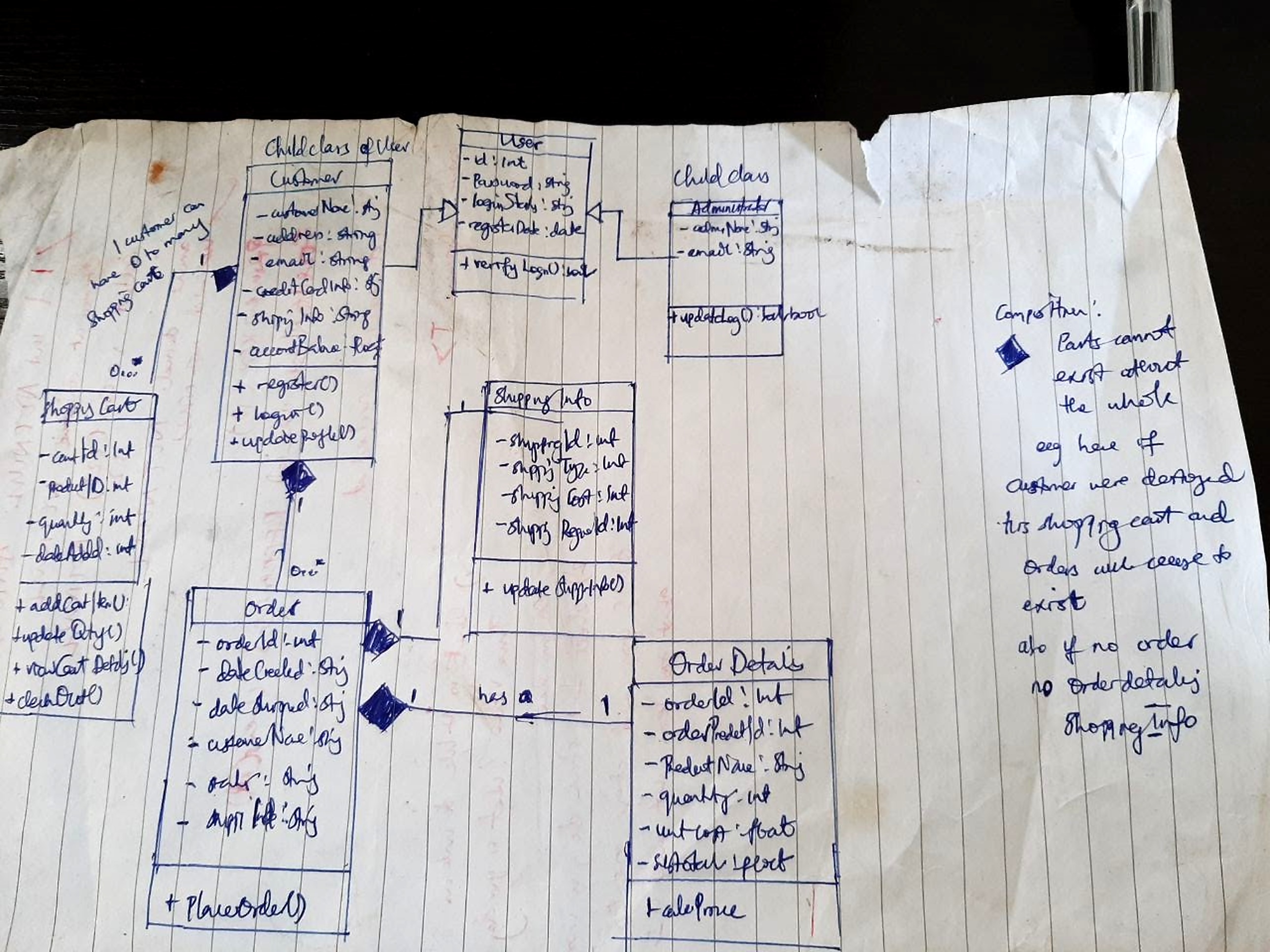
I found this UML diagram in one of my old hardcopy notes and decided to move my System Design scribblings online.
Generally, there are two tiers of System Design knowledge.
- Low Level Design
- High Level Design
Low-Level Design
In this context, Low Level Design (hereafter referred to as LLD), has to do with the structure or implementation of a particular system or a feature in a system. i.e How the various classes fit together etc.
This is a great point to bring up UML Class diagrams as this is a good way to illustrate how classes/objects are related to each other in a system.
I came across LucidChart on Youtube a few years ago when I wanted to learn about UML. It turns out they also have a tool to draw UML diagrams. See in the reference section.
Points to note about UML Diagrams and Interaction of Objects OOP
.
-
Composition indicates that the “composed” cannot continue to exist without the “composer”. For instance, in an e-commerce system, if a Customer was destroyed/deleted (Composer), that customer’s shopping cart and orders will in a sense, cease to exist.
-
Composition is generally represented by a dark filled diamond besides the composer object with a line drawn to touching the composed object.
-
Composition is typically used to represent has a/many . i.e (1 - 1) vs (1 - 0…*)
-
A child class is usually looking up in form of a clear headed arrow to the parent class.
-
A class has three sections namely a) Class name b) Class properties usually private c) Class methods of different both visibility types
-
’-‘ infront of a property indicates it is private whereas ‘+’ signigies that it is public.
Notes about Java and Misc.
- An abstract class cannot be instatiated but can be subclassed.
- An abstract class can have 0 to several abstract methods.
- A non-abstract class cannot have abstract methods.
- An abstract method is defined without a body like so :
public abstract int myMethod(int n1, int n2); - In Java, a class has to implement all the methods of an interface except it is an abstract class
Notes about Swift
- Unlike in C++ where properties of structs are public whereas those of classes are private, in swift, structs are passed by value whereas classes are passed by reference (i.e the address in memory)
References
Note to reader:
It is not enough to regurgitate these points. It will be beneficial to know the how and why. Also this is not a Lucid Chart Advert dump.
I'll scribble out High-Level System Design stuff in another note so that resource can grow as well
.
